Medium format cameras are renowned for their exceptional image quality and detail, making them a popular choice for both professional photographers and videographers. However, optimizing these cameras for video recording requires a comprehensive understanding of their features and settings.
In this article, we will explore various strategies to maximize the potential of your medium format camera for video recording, ensuring you achieve the highest quality results.
Keep Reading: long exposure medium format photos
What are Medium Format Cameras
| Image | Product | Price |
|
Our Pick
1

|
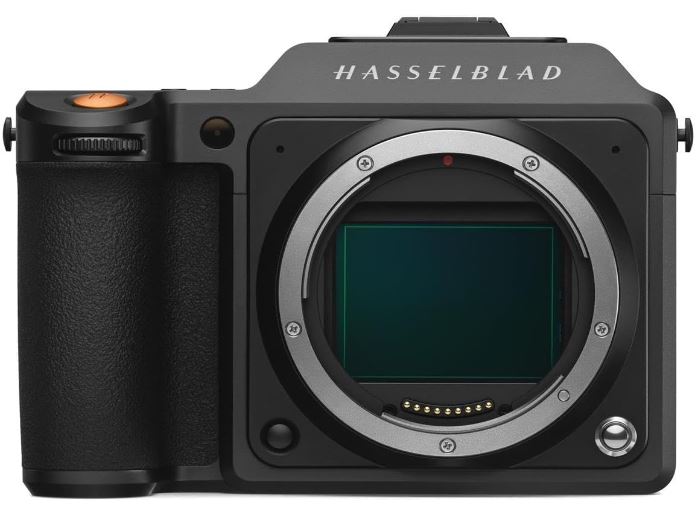
Hassel X1D |
|
|
2

|
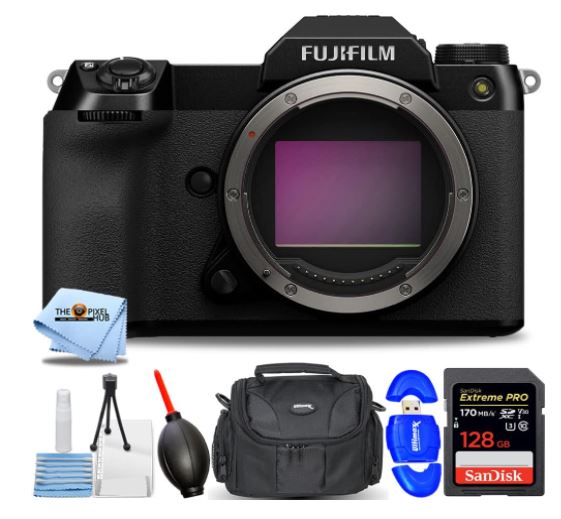
Fujifilm GFX |
|
|
3

|
Pentax 6457 |
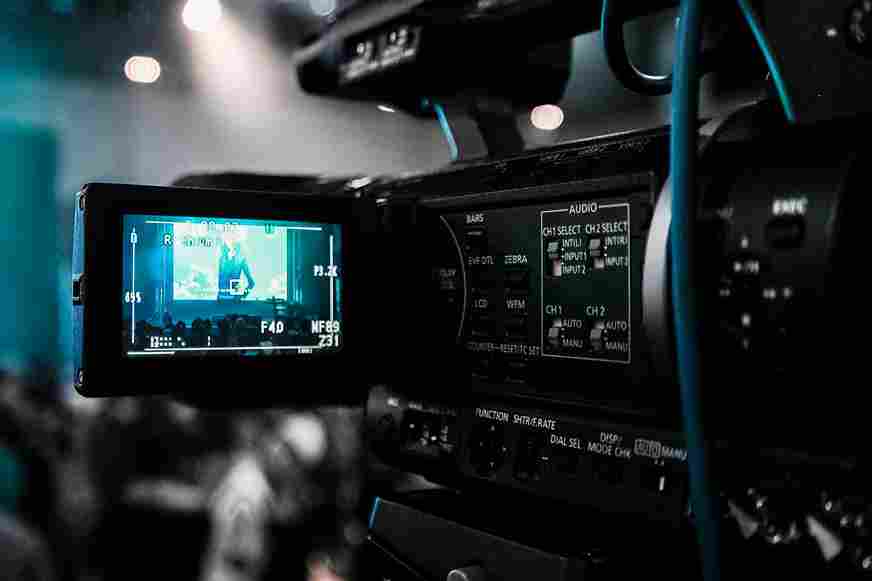

Medium format cameras offer a larger sensor size compared to traditional full-frame or crop-sensor cameras. This larger sensor provides superior image quality, greater dynamic range, and better low-light performance. When used for video recording, these advantages translate into more detailed and immersive footage.
Choosing the Right Medium Format Camera for Video
Not all medium format cameras are created equal when it comes to video recording. When selecting a camera for video work, consider the following key factors:
- Resolution: Higher-resolution sensors capture more detail, which is crucial for high-quality video. Look for cameras that offer 4K or higher resolution recording.
- Frame Rate: For smooth motion and cinematic effects, choose a camera that supports high frame rates (e.g., 60fps or higher).
- Bit Depth and Color Sampling: Cameras with higher bit depth (10-bit or more) and superior color sampling (4:2:2 or better) provide more flexibility in post-production color grading.
Camera Settings for Optimal Video Quality
To achieve the best results from your medium format camera, it’s essential to configure it correctly for video recording. Here are some critical settings to adjust:
Resolution and Frame Rate
Set your camera to the highest resolution available, such as 4K, to ensure crisp, detailed video. Additionally, choose an appropriate frame rate based on your project’s needs. Common frame rates include 24fps for a cinematic look, 30fps for standard video, and 60fps or higher for slow-motion effects.
Shutter Speed
The shutter speed should be set to twice the frame rate for natural motion blur. For instance, if you’re shooting at 24fps, set the shutter speed to 1/50s. This rule helps maintain a natural motion blur that replicates how our eyes perceive movement.
ISO Settings
Keep ISO as low as possible to minimize noise in your footage. Medium format cameras generally perform well in low-light conditions, but maintaining a lower ISO ensures cleaner, more professional results.
White Balance
Set a consistent white balance for your shoot to avoid color shifts and maintain color accuracy throughout your footage. Avoid using auto white balance, as it can cause unwanted color changes.
Picture Profile
Choose a flat or log picture profile if your camera supports it. These profiles capture more dynamic range and allow for greater flexibility during color grading in post-production.
Utilizing Lenses for Video Recording
The choice of lens plays a significant role in video quality. Consider the following when selecting lenses for your medium format camera:
- Focal Length: Longer focal lengths offer better subject isolation and a shallower depth of field, while shorter focal lengths provide wider views. Choose lenses based on the type of shots you need.
- Aperture: Lenses with a wide maximum aperture (e.g., f/2.8 or lower) allow more light to enter the camera, which is beneficial for low-light recording and achieving a shallow depth of field.
- Optical Stabilization: Lenses with optical stabilization can help reduce camera shake, resulting in smoother footage.
Audio Considerations
High-quality audio is essential for professional video production. Here are some tips to ensure excellent audio quality:
- External Microphones: Use external microphones for better audio capture compared to built-in camera microphones. Lavalier mics, shotgun mics, or handheld mics can be used based on your recording environment.
- Audio Levels: Monitor and adjust audio levels to prevent distortion and ensure clear sound. Most cameras provide audio level meters for this purpose.
- Wind Protection: If recording outdoors, use windshields on your microphones to reduce wind noise.
Lighting Techniques
Proper lighting is crucial for achieving high-quality video. Here’s how to effectively use lighting with your medium format camera:
- Three-Point Lighting: This technique involves using a key light, fill light, and backlight to create a well-lit scene with balanced shadows and highlights.
- Natural Light: Utilize natural light sources when possible, and use reflectors or diffusers to control and soften the light.
- Lighting Equipment: Invest in high-quality lighting equipment to ensure consistent and professional results.
Post-Production Workflow
After recording, the post-production process is where your footage truly comes to life. Here’s how to maximize your medium format video footage in post-production:
- Color Grading: Apply color grading to enhance the visual appeal of your footage. Use tools such as LUTs (Look-Up Tables) or manual color correction to achieve the desired look.
- Editing Software: Utilize professional video editing software that supports high-resolution and high bit depth formats, such as Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, or Final Cut Pro.
- Resolution and Export Settings: Export your final video in the highest resolution possible, and choose appropriate codecs for distribution, such as H.264 for web or ProRes for archival.
Conclusion
Optimizing your medium format camera for video recording involves understanding the camera’s capabilities, adjusting settings for video quality, choosing the right lenses, and ensuring high-quality audio and lighting. By following these guidelines, you can harness the full potential of your medium format camera and produce exceptional video content.